Security Cameras
There are several types of security cameras, each designed for specific applications and environments. Here are the main types:
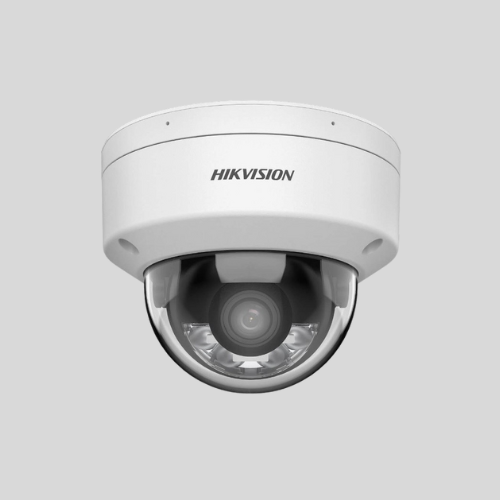

Indoor Cameras
- Used for monitoring inside homes or businesses.
- Often compact and designed to blend with home decor.
- Can be wired or wireless.
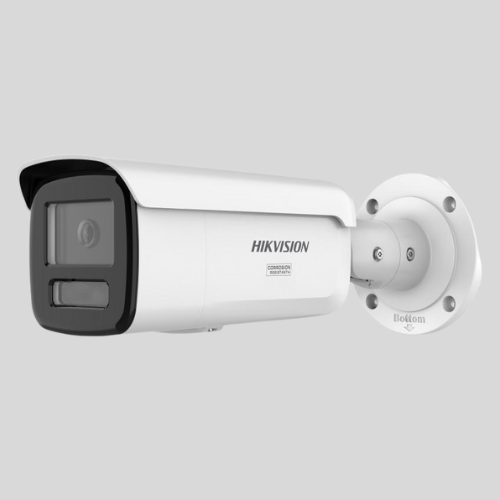

Outdoor Cameras
- Built to withstand weather conditions (rain, snow, heat).
- Often equipped with night vision and motion detection.
- Usually more durable than indoor cameras.

Wired Cameras
- Require physical cables for power and data transmission.
- Offer reliable connections without interference.
- Ideal for permanent installations.

Wireless Cameras
- Use Wi-Fi or other wireless signals to transmit footage.
- Easier to install than wired cameras.
- May have battery or solar power options.
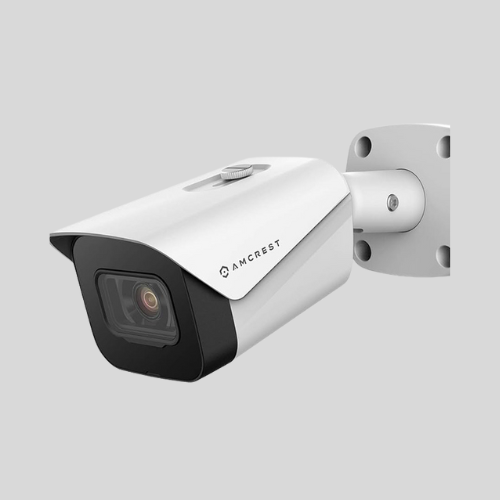

IP Cameras (Internet Protocol Cameras)
- Connect to a network and can be accessed remotely via apps.
- Offer high-definition video quality.
- Can be wired (Ethernet) or wireless.
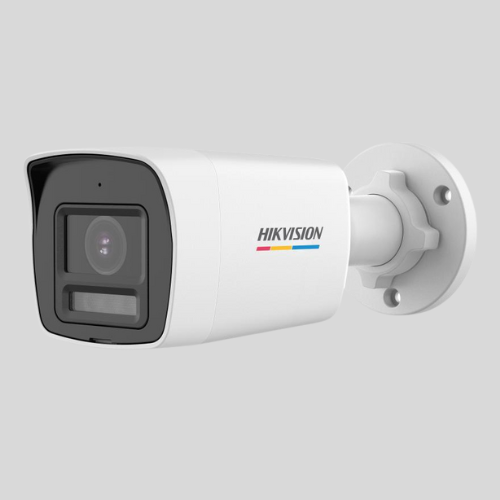

Analog Cameras
- Older technology that transmits video via coaxial cables
- Requires a DVR (Digital Video Recorder) for storage.
- Lower resolution compared to IP cameras.
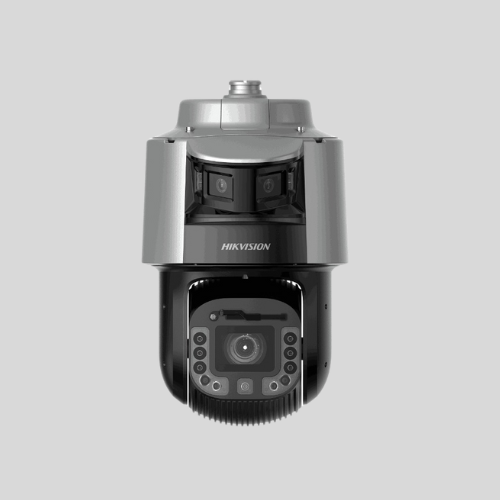

PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) Cameras
- Can move horizontally (pan), vertically (tilt), and zoom in/out.
- Ideal for large areas needing flexible monitoring.
- Often used in public surveillance.
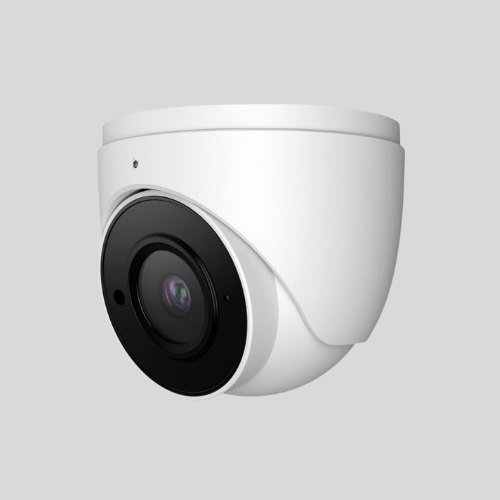

Dome Cameras
- Enclosed in a dome-shaped casing, making it hard to determine the direction of the lens.
- Common in businesses and retail stores.
- Can be vandal-resistant.
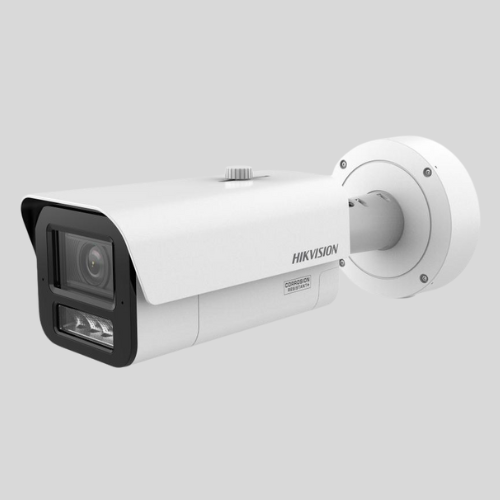

Bullet Cameras
- Cylindrical shape, often used outdoors.
- Long-range visibility.
- Easy to mount on walls or ceilings.
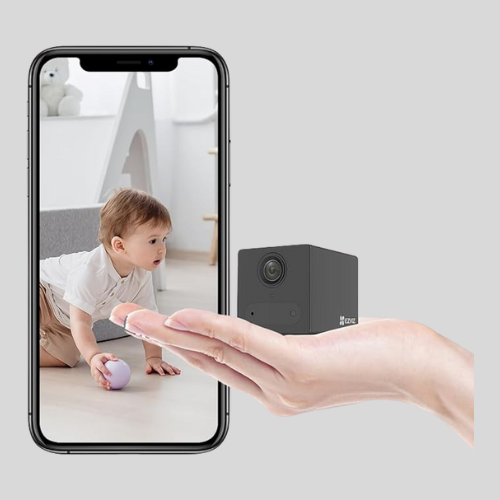

Hidden/Spy Cameras
- Small and disguised as everyday objects (e.g., clocks, smoke detectors).
- Used for covert surveillance.
- Often come with motion detection and night vision.
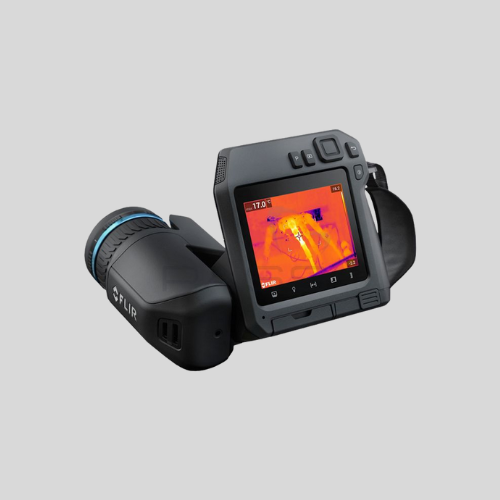

Thermal Cameras
- Detect heat signatures rather than visible light.
- Useful for low-light or complete darkness.
- Common in security and industrial applications.
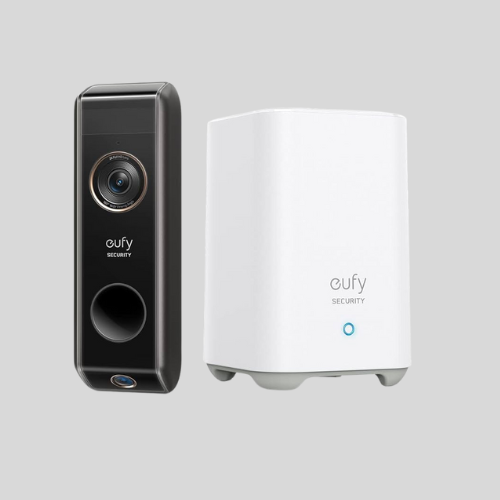

Doorbell Cameras
- Installed at front doors to monitor visitors.
- Often include two-way audio and motion alerts.
- Integrated with smart home systems.
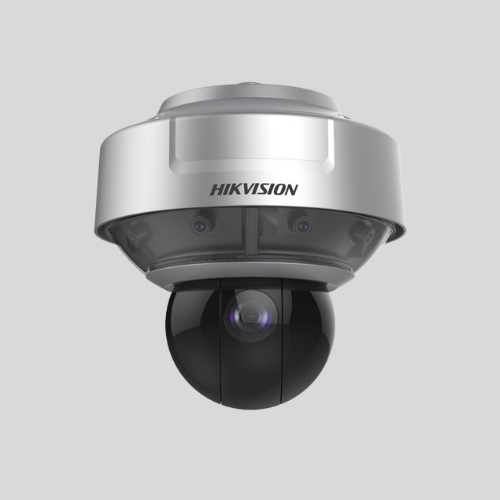

360-Degree Cameras
- Provide a full panoramic view without blind spots.
- Used in large areas for comprehensive monitoring.
- Some models offer fisheye viewing options.
Time attendances machines
Time attendance machines are used to track employee work hours, manage attendance records, and enhance workforce efficiency. These machines automate attendance tracking, reducing errors and improving payroll management.
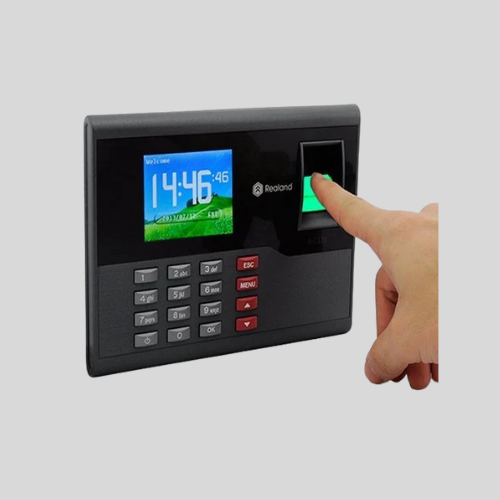

Biometric Attendance Machines
- Use fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scanning, or palm recognition.
- Prevents buddy punching (one employee clocking in for another).
- Highly secure and reliable for workforce management.
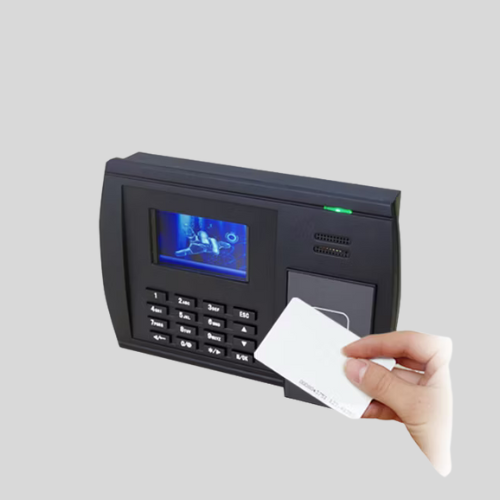

RFID/Proximity Card Attendance Machines
- Employees swipe or tap a card to register attendance.
- Quick and easy to use, suitable for large organizations.
- Can be integrated with access control systems.
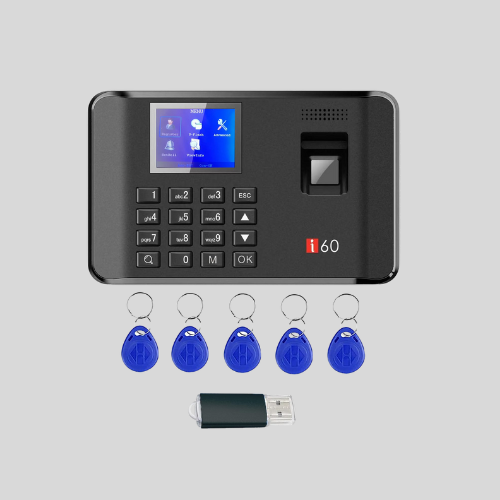

PIN or Password-Based Attendance Machines
- Employees enter a unique PIN or password to mark attendance.
- Less secure as passwords can be shared.
- Cost-effective but prone to manipulation.
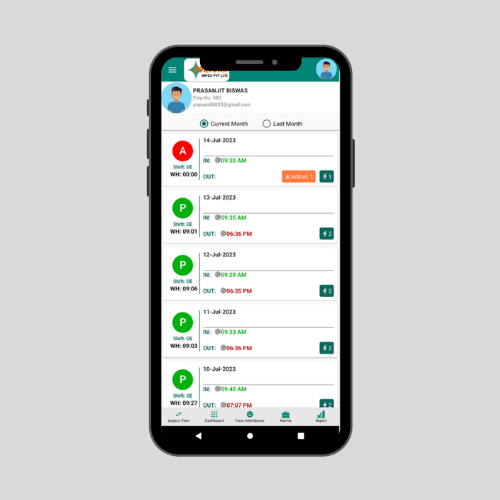
Mobile App-Based Attendance Systems
- Employees check in via a mobile app with GPS tracking.
- Useful for remote workers and field employees.
- Can integrate with HR and payroll software.
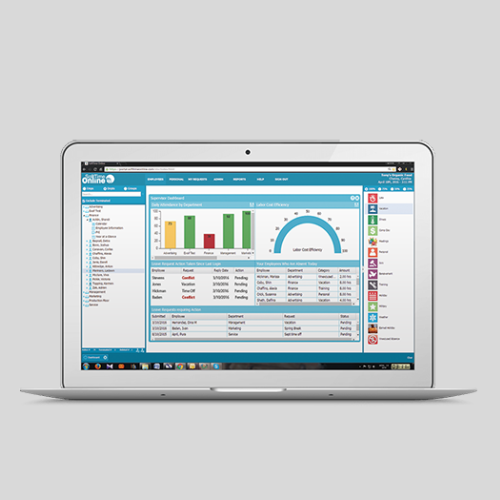
Web-Based Attendance Systems
- Employees log in through an online portal.
- Suitable for hybrid or remote work environments.
- Provides real-time attendance data to managers.
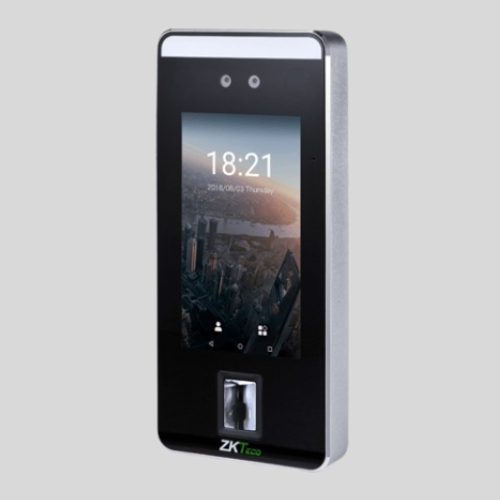

Face Recognition Attendance Machines
- Uses AI-powered facial recognition for fast and contactless attendance.
- Highly secure and eliminates the need for physical touch.
- Works well in high-security environments.
Uses of Time Attendance Machines
- Employee Attendance Tracking – Monitors check-in and check-out times.
- Payroll Processing – Automates salary calculations based on work hours.
- Overtime Management – Tracks extra working hours accurately.
- Workplace Security – Prevents unauthorized access to office premises.
- Compliance & Legal Documentation – Ensures adherence to labor laws and company policies.
- Productivity Enhancement – Helps analyze employee punctuality and efficiency.
Integration with Other Systems
- HR & Payroll Software: Automates salary processing.
- Access Control Systems: Restricts entry to authorized personnel.
- Cloud & Mobile Apps: Enables remote monitoring of attendance data.
Access control devices
Access control devices regulate and restrict entry to buildings, rooms, or areas by verifying an individual’s identity. They enhance security, track access history, and prevent unauthorized entry.

Biometric Access Control Systems
- Uses fingerprint, facial recognition, iris scan, or palm vein recognition.
- Highly secure and prevents unauthorized access.
- Common in high-security areas like data centers and government buildings.
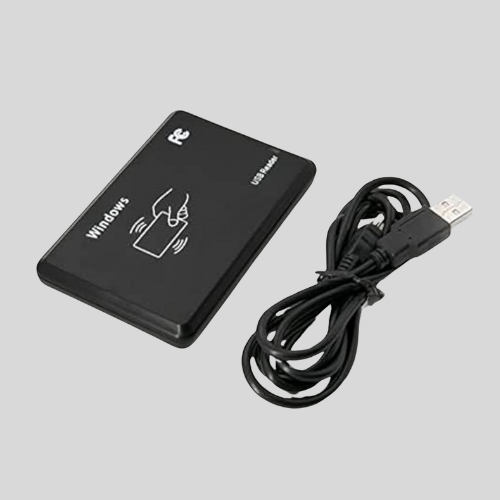

RFID/Proximity Card Readers
- Employees or visitors use an RFID card or key fob for access.
- Works with NFC (Near Field Communication) and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology.
- Common in offices, hotels, and residential complexes.

Keypad & PIN Code Entry Systems
- Users enter a PIN or passcode to gain access.
- Affordable and easy to use but less secure if codes are shared.
- Used in offices, homes, and warehouses.
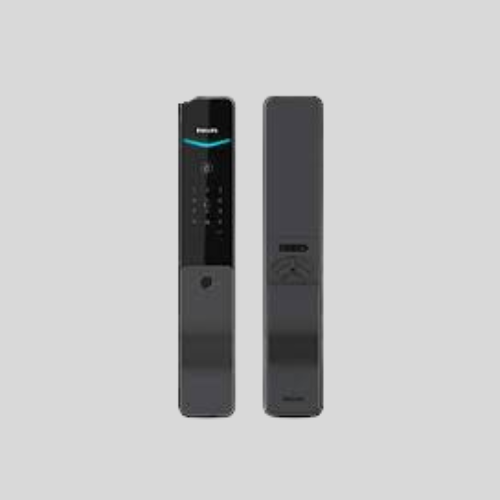

Smart Locks
- Operated via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or mobile apps.
- Can be integrated with smart home systems like Alexa and Google Assistant.
- Suitable for homes, apartments, and Airbnbs.
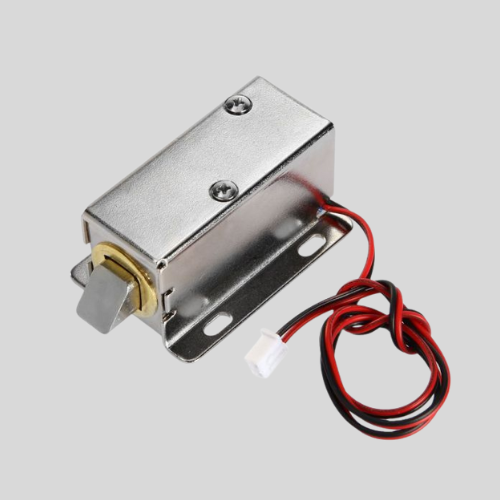

Magnetic & Electric Door Locks
- Use electromagnets or electric strikes to lock/unlock doors.
- Often used with keycards, biometrics, or PIN-based access systems.
- Found in commercial buildings and secured facilities.
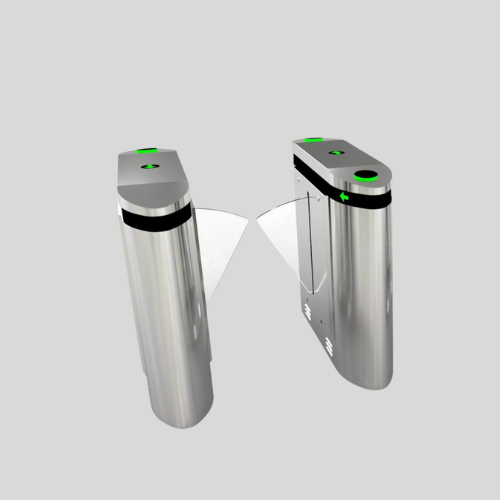

Turnstiles & Barrier Gates
- Control pedestrian and vehicle access at entry points.
- Used in stadiums, metro stations, and corporate offices.
- Can be integrated with biometric or RFID systems.
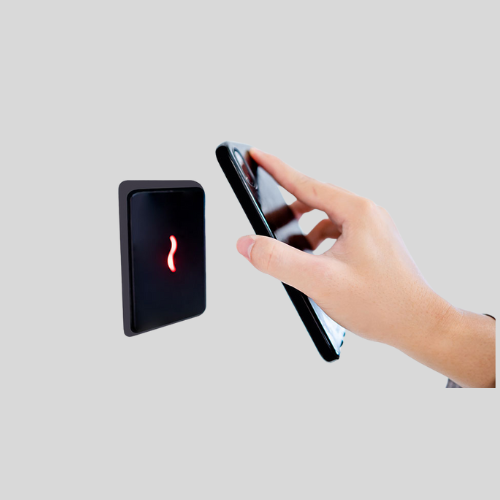

Mobile-Based Access Control
- Uses smartphone apps, QR codes, or Bluetooth for entry.
- Ideal for contactless access in offices and hotels.
- Works well in cloud-based access control systems.
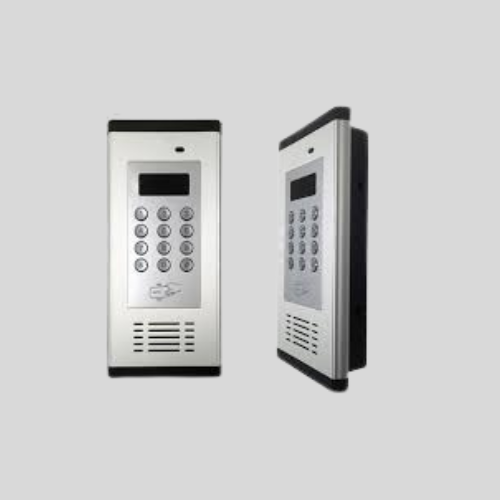

Intercom Systems with Access Control
- Allows audio/video communication before granting access.
- Used at gated communities, apartment buildings, and offices.
- Can integrate with mobile apps for remote access approval.
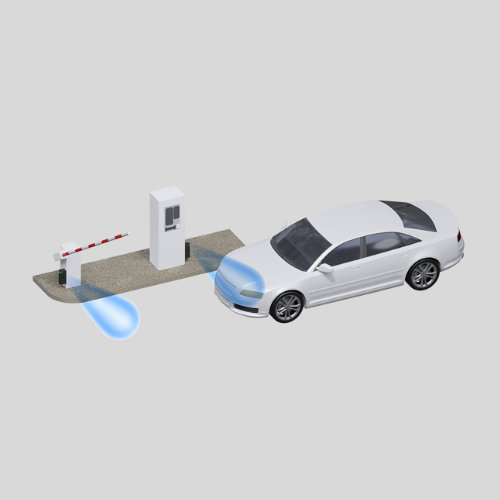

License Plate Recognition (LPR) Systems
- Uses cameras to scan and verify vehicle license plates.
- Used in parking lots, toll booths, and gated communities.
- Can integrate with barrier gates for automatic entry.
Uses of Access Control Devices
- Enhances security by restricting unauthorized entry.
- Monitors and records access history for audits.
- Prevents internal threats like employee fraud or data breaches.
- Improves convenience with touchless and automated access.
- Integrates with surveillance and alarm systems for complete security.
Security Gates
Security gates are used to control access to properties, buildings, and restricted areas. They enhance security by preventing unauthorized entry and can be integrated with access control systems.

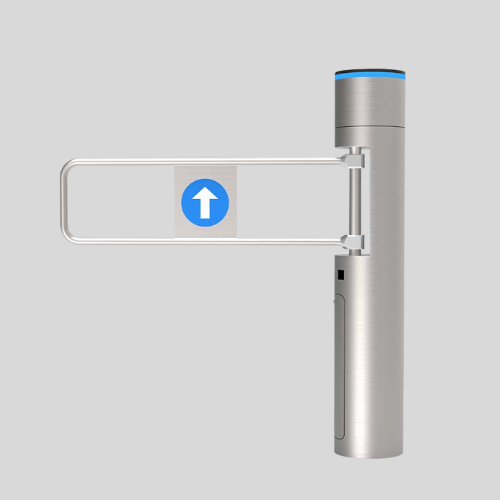
Swing Gates
- Open like a traditional door (inward or outward).
- Can be manual or automatic (motorized).
- Used in residential areas, office buildings, and industrial premises.

Sliding Gates
- Slide horizontally along a track to open/close.
- Ideal for narrow spaces where swing gates aren’t feasible.
- Common in commercial buildings, warehouses, and gated communities.

Barrier Arm Gates (Boom Gates)
- Feature a long arm that lifts to allow or restrict vehicle access.
- Often used in parking lots, toll booths, and checkpoints.
- Can be integrated with RFID, license plate recognition (LPR), and ticketing systems.
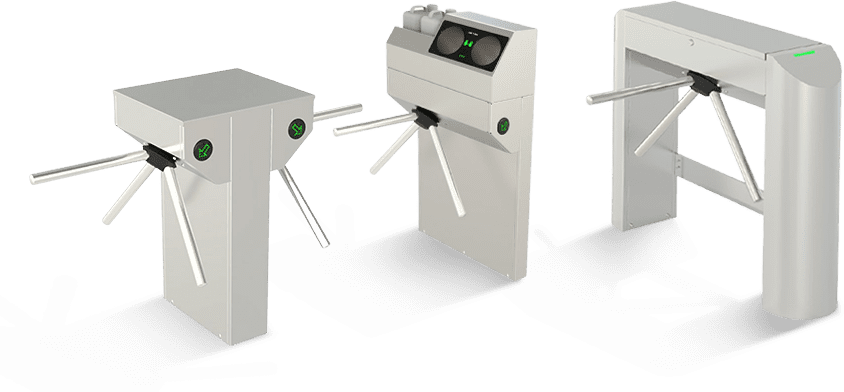
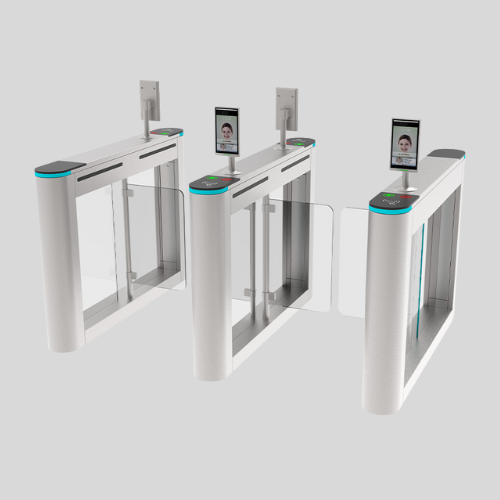
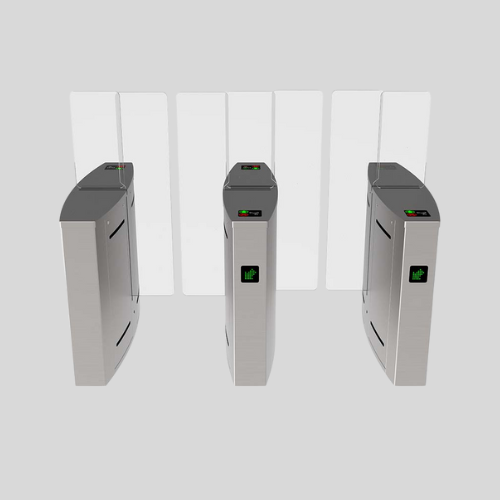
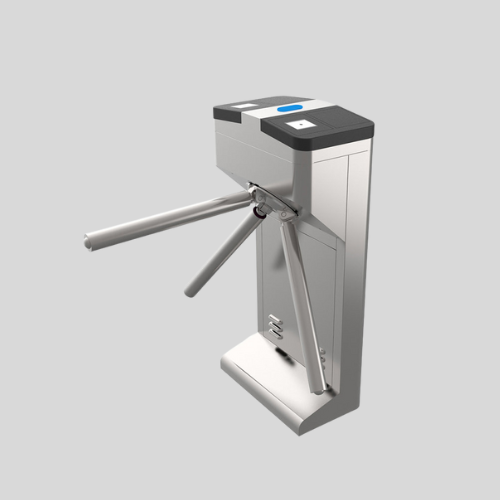
Turnstile Gates
- Control pedestrian access using rotating arms.
- Can be waist-high or full-height for added security.
- Common in stadiums, metro stations, offices, and secured facilities.
Bi-Folding Gates
- Feature two panels that fold together when opening.
- Open and close quickly, making them ideal for high-traffic areas.
- Used in commercial buildings, warehouses, and military bases.
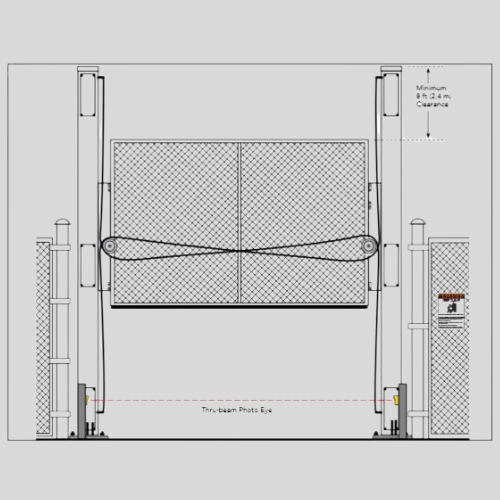
Vertical Lift Gates
- Lift vertically like a garage door instead of swinging or sliding.
- Used where there is limited side space.
- Common in industrial zones and military facilities.

Retractable (Telescopic) Gates
- Made of multiple sections that collapse or extend as needed.
- Provide adjustable security, ideal for temporary or semi-permanent setups.
- Common in factories, warehouses, and event venues.
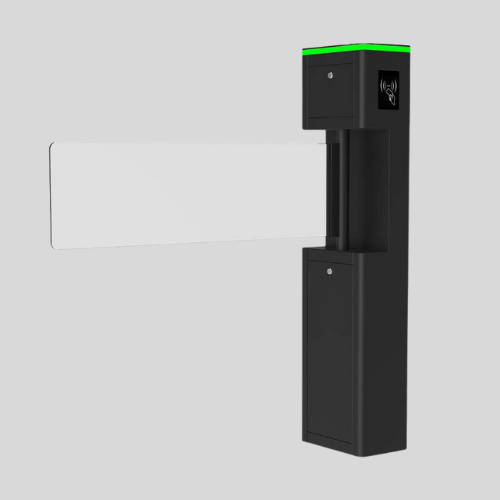
Smart & Automated Security Gates
- Controlled via remote, keypad, smartphone apps, or sensors.
- Often integrated with CCTV cameras, intercoms, and biometric access systems.
- Used in modern homes, businesses, and high-security areas.
Uses of Security Gates
- Restricts unauthorized access to residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
- nhances safety by preventing vehicle intrusions and unauthorized pedestrian entry.
- Improves traffic control in parking lots, toll stations, and gated communities.
- Integrates with access control systems for added security.
- Provides convenience with remote or automated operation.
